Calling other programming languages
java (.jar)python (.py)php (.php)js (.js)BeanShell (.bsh)go (.go)shell (.sh)ruby (.rb)lua (.lua)Calling an external program
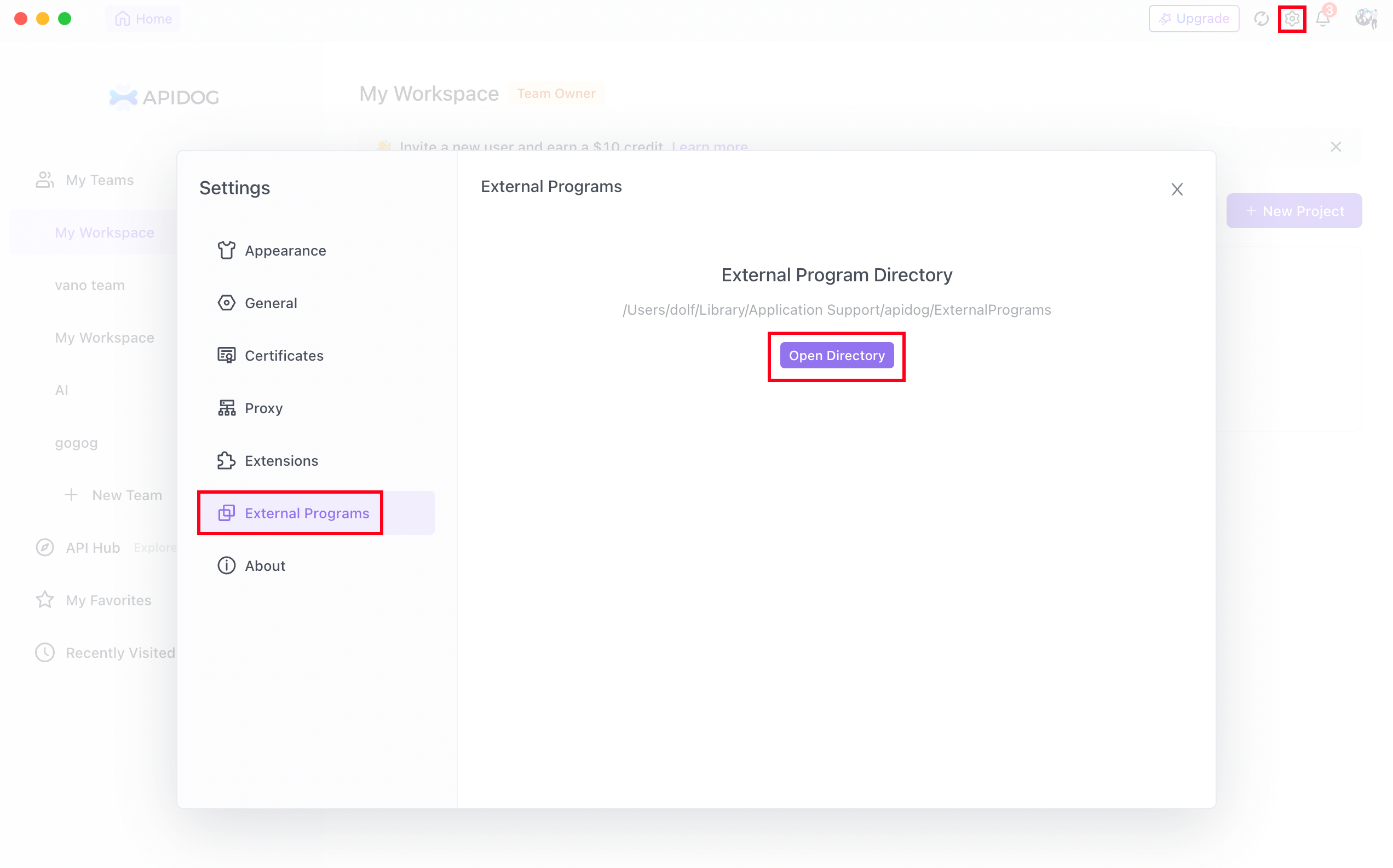
1.
2.
3.
pm.execute('com.apicat.Base64EncodeDemo.jar', ['abc','bcd']), the actual executed command is java -jar "com.apicat.Base64EncodeDemo.jar" "abc" "bcd".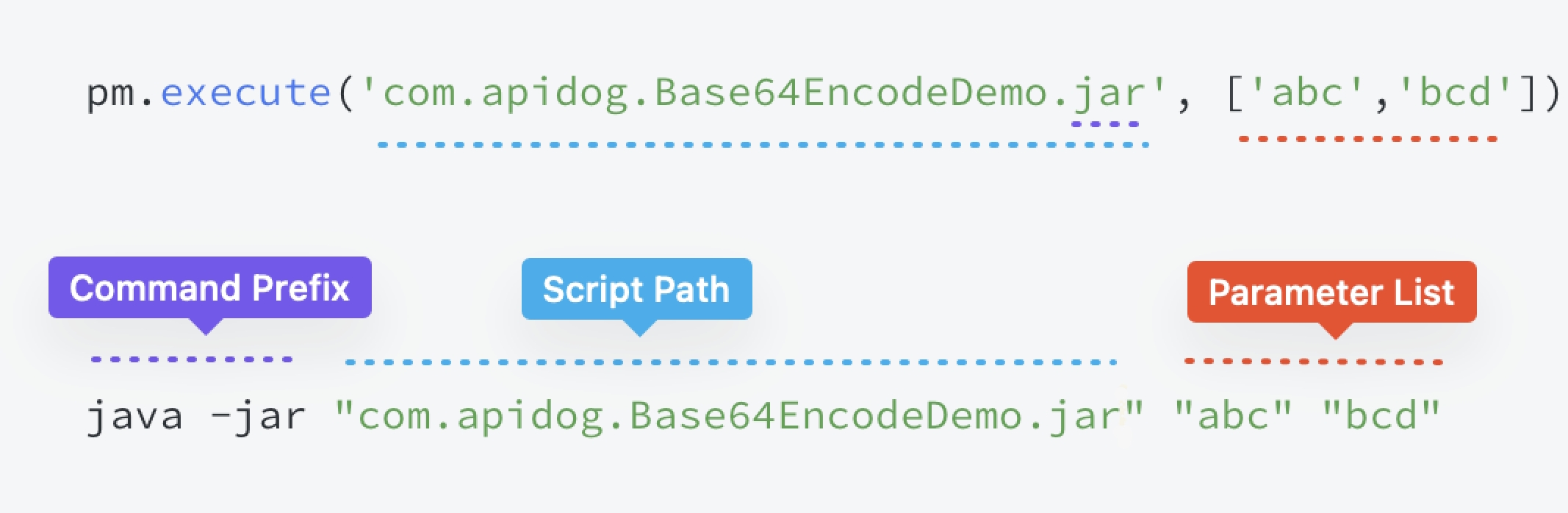
| Language | Command Prefix | File Extension |
|---|---|---|
| Java | java -jar | .jar |
| Python | python | .py |
| PHP | php | .php |
| JavaScript | node | .js |
| BeanShell | java bsh.Interpreter | .bsh |
| Go | go run | .go |
| Shell | sh | .sh |
| Ruby | ruby | .rb |
| Lua | lua | .lua |
| Rust | cargo run | .rs |
| Python | python | .py |
API
pm.executeAsync
filePath string External program pathargs string[] Parameters. When calling specified methods in a jar package, JSON.stringify will be used for conversion. Except for that, non-string types will be implicitly converted to string.options Objectcommand string The execution command of the external program, the first part of "command prefix" is the execution command. Optional, default value is inferred automatically (see "command prefix" table above), can be customized to any program.cwd string Working directory of the subprocess. Optional, default is "External Programs Directory".env Record<string, string> Environment variables of the subprocess. Optional, default is {}.windowsEncoding string Encoding used on Windows system. Optional, default is "cp936".className string Specify the class name to call in the jar package, e.g. "com.apicat.Utils". Optional, see Call specified methods in jar packages for details.method string Specify the method name to call in the jar package, e.g. "add". Optional (required if className has value), see Call specified methods in jar packages for details.paramTypes string[] Specify the parameter types of the method to call in the jar package, e.g. ["int", "int"]. Optional, default is inferred automatically based on parameters, see Call specified methods in jar packages for details.Usage of
command parameterpython to execute .py files. If python3 is already installed on the computer, command can be specified as python3.pm.execute
pm.executeAsync instead, See Code migration instructions for details.pm.execute(filePath, args, options)filePath string External program pathargs string[] Parameters. When calling specified methods in a jar package, JSON.stringify will be used for conversion. Except for that, non-string types will be implicitly converted to string.options ObjectwindowsEncoding string Encoding used on Windows system. Optional, default is "cp936".className string Specify the class name to call in the jar package, e.g. "com.apicat.Utils". Optional, see Call specified methods in jar packages for details.method string Specify the method name to call in the jar package, e.g. "add". Optional (required if className has value), see Call specified methods in jar packages for details.paramTypes string[] Specify the parameter types of the method to call in the jar package, e.g. ["int", "int"]. Optional, default is inferred automatically based on parameters, see Call specified methods in jar packages for details.Execution and Logs
Shell/CMD to debug.TIP
pm.execute treats execution as failed when there is content in stderr. This causes some programs to fail when outputting warnings or error messages. pm.executeAsync changes to use the exit code of the process to determine if the execution failed.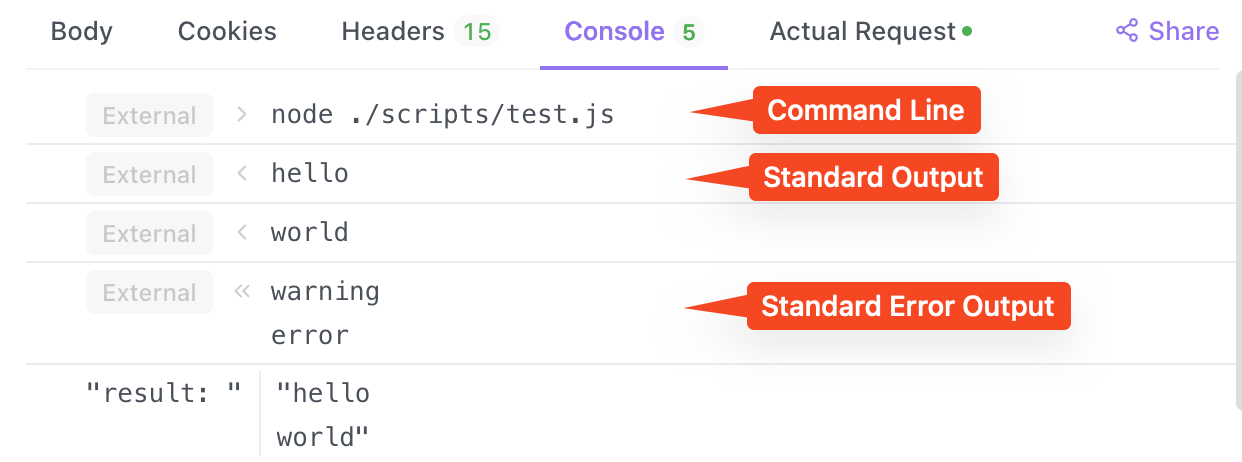
Input and output of external programs
Parameters
pm.executeAsync('add.js', [2, 3]), the actual executed command is node add.js 2 3. To get the parameters in the external script add.js:TIP
1.
2.
Return value
const result = await pm.executeAsync('add.js', [2, 3]), the result can be returned by:1.
2.
3.
4.
Throwing errors
1.
2.
console.error('Error') only prints to stderr instead of throwing an error. Consider this while using other languages too.Debug information
pm.executeAsync uses exit code instead of stderr to determine success, stderr can be used to print debug information without affecting execution.TIP
1.
pm.executeAsync supports this way of printing debug info.2.
Migrate from pm.execute to pm.executeAsync
pm.executeAsync is Promise type, execute cannot be directly changed to executeAsync. But you can use async/await to migrate with minimal changes.TIP
1.
execute to executeAsync2.
await before function callCall specified methods in .jar packages
TIP
options.className is specified, it will override the default behavior and call the specified method in the jar instead.<app-dist>/assets/JarExecuter-1.1.0-jar-with-dependencies.jar is the built-in executor, responsible for finding the method com.apicat.Test.combine(String,String) in the user program ./scripts/jar-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar through reflection, and calling it with parameters (JSON string) "hello" and "world".TIP
paramTypes is optional. If not specified, types will be inferred automatically based on parameters. Integers are inferred as "int", floats as "double", booleans as "boolean", strings as "String", arrays are inferred based on the first element, e.g. [3] is inferred as "int[]", [3.14] as "double[]", etc.If the inferred types do not match the actual parameter types of the called method,
paramTypes needs to be specified manually.Supported values in
paramTypes array: "Number"、"int"、"Integer"、"long"、"Long"、"short"、"Short"、"float"、"Float"、"double"、"Double"、"boolean"、"Boolean"、"String"、"Number[]"、"int[]"、"Integer[]"、"long[]"、"Long[]"、"short[]"、"Short[]"、"float[]"、"Float[]"、"double[]"、"Double[]"、"boolean[]"、"Boolean[]"、"String[]"paramTypes in the example above can be omitted:Examples
1. PHP program
2. Jar program
Common issues
1. Some programs require project config files and will error if missing
could not find `Cargo.toml` in `<...>/ExternalPrograms` or any parent directorygo.mod file not found in current directory or any parent directory; see 'go help modules'cwd.2. MacOS has built-in Python 3 but no Python 2
command to "python3".3. Command xxx not found
4. Calling external scripts prints garbled on some Windows systems
windowsEncoding to 'utf-8'Modified at 2025-09-03 10:06:09